Refinancing is a financial strategy that can offer substantial benefits to individuals and businesses alike. Whether you’re looking to lower your monthly mortgage payments, reduce interest rates on your student loans, or optimize your business debt, refinancing can be a powerful tool. In this article, we will explore the concept of refinancing, its various forms, and how it works.
What is Refinancing?
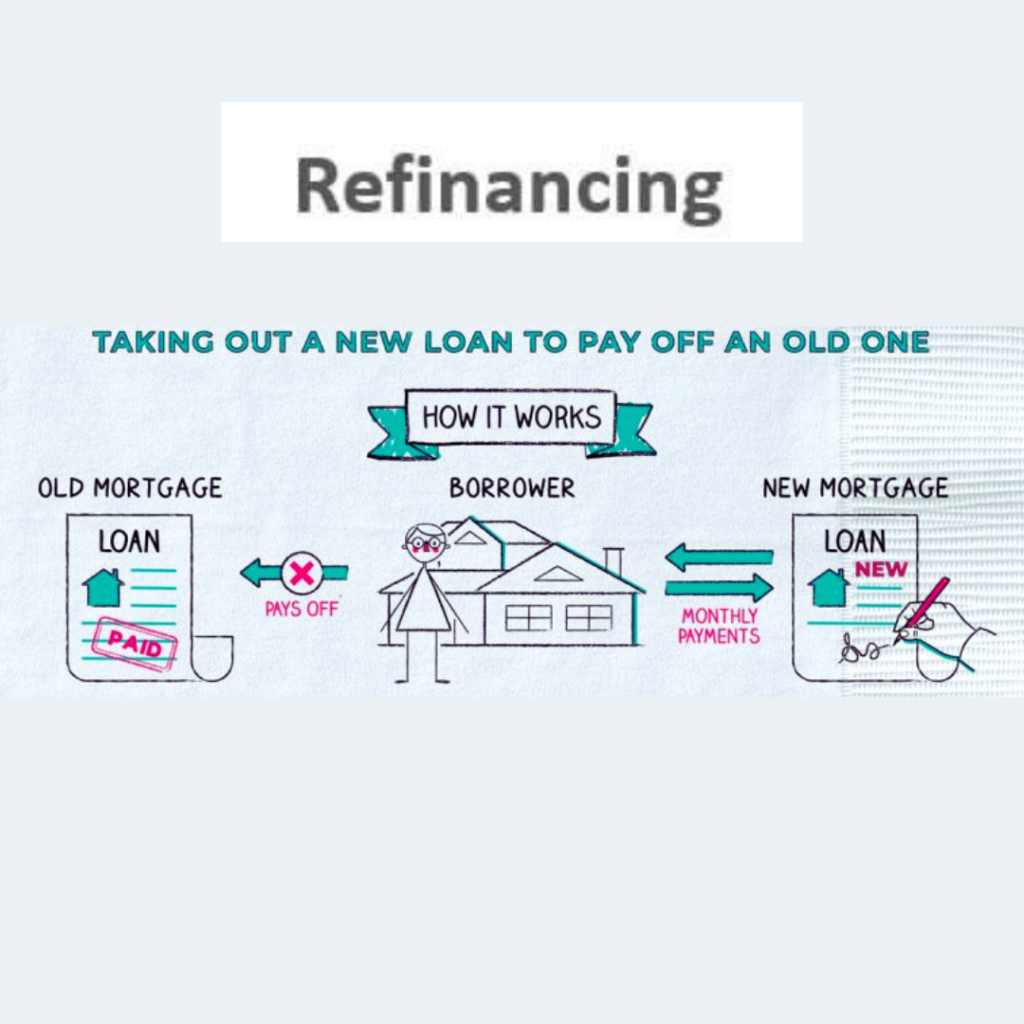
Refinancing is the process of replacing an existing loan or debt obligation with a new one that has different terms, often to obtain better interest rates, lower monthly payments, or other favorable conditions. It essentially allows borrowers to reset the terms of their debt, which can be advantageous in various financial situations.
Also Read: What are the factors that affect personal loan amounts?
How Does Refinancing Work?
To understand how refinancing works, let’s break down the process into a few key steps:
- Assessment: First, you should assess your current financial situation and the terms of your existing loan or debt. Determine your objectives for refinancing, such as reducing monthly payments, lowering interest rates, or shortening the loan term.
- Research and Compare: Shop around for lenders or financial institutions that offer refinancing options that align with your goals. Compare interest rates, fees, and terms from multiple lenders to find the most favorable offer.
- Application: Once you’ve identified a suitable lender, you’ll need to complete a refinancing application. Be prepared to provide documentation of your financial history, income, and credit score. The lender will use this information to assess your eligibility and determine the terms they can offer you.
- Approval and Underwriting: After submitting your application, the lender will review your financial information and perform a credit check. They may request additional documentation or verification. The underwriting process is crucial in assessing your risk as a borrower and determining the terms of your new loan.
- Closing: If your application is approved, you’ll proceed to the closing phase. During closing, you’ll sign the new loan agreement, and the lender will disburse the funds to pay off your existing debt(s). Your old loan(s) will be closed, and you’ll begin making payments on the new loan according to its terms.
Types of Refinancing
There are several common types of refinancing, each tailored to specific financial needs:
- Mortgage Refinancing: This involves replacing your current mortgage with a new one, often with more favorable terms. Common reasons for mortgage refinancing include lowering interest rates, reducing monthly payments, or switching from an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) to a fixed-rate mortgage.
- Student Loan Refinancing: Individuals with student loans can refinance to obtain lower interest rates, extend their repayment terms, or consolidate multiple loans into a single, more manageable loan.
- Auto Loan Refinancing: Refinancing an auto loan can help you secure a lower interest rate, potentially reducing the overall cost of your vehicle and lowering monthly payments.
- Business Loan Refinancing: Businesses can refinance existing loans to improve cash flow, lower interest expenses, or extend repayment terms. It’s a valuable strategy for optimizing a company’s debt structure.
- Personal Loan Refinancing: If you have high-interest personal loans, refinancing can help you secure a lower rate, reduce monthly payments, and save money over the life of the loan.
You May Also Read: What is a Bridge Loan?
Benefits of Refinancing
Refinancing offers various benefits, including:
- Lower Interest Rates: Refinancing can lead to lower interest rates, resulting in reduced overall interest expenses.
- Lower Monthly Payments: Extending the loan term or securing a lower interest rate can lead to smaller monthly payments, making it easier to manage your finances.
- Debt Consolidation: Combining multiple loans into a single, more manageable loan can simplify your financial life.
- Improved Cash Flow: Refinancing can free up cash flow, allowing you to allocate resources to other financial goals or investments.
- Shortened Loan Term: Some borrowers choose to refinance to shorten the loan term and pay off their debt faster, saving on interest costs.
Does refinancing affect credit score?
Refinancing can also impact a borrower’s credit rating in the beginning. However, in the long run, you could enhance their credit score by making sure they make well-timed payments and cope with the debt.
When switching to a brand new lender, besides thinking about the hobby fee on the brand new loan, one should compare elements, which include mortgage tenure and hidden costs relevant to refinancing.
